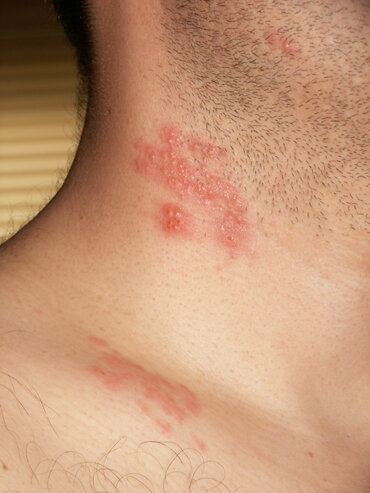
Shingles or as known as Herpes zoster is a localised, blistering and painful rash caused by reactivation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Herpes zoster is also called shingles.
If you have had chickenpox (varicella) before you may also develop shingles (herpes zoster). Shingles can occur in childhood but is much more common in adults, especially the elderly. If you have had shingles before, the chances of getting a second episode is about 1% .
Herpes Zoster often affect people with weak immunity.
What causes Shingles ?
After primary infection, varicella remains dormant in your nerves for years before it is reactivated and migrates down your sensory nerves to the skin to cause shingles.
Some triggering factors are:
- Pressure on the nerve roots
- Radiotherapy at the level of the affected nerve root
- Spinal surgery
- An infection
- An injury (not necessarily to the spine)
Clinical Features
Shingles is a painful blistering rash, symptoms include:
- Tingling, burning sensation in the area. This is where a painful blistering rash will appear
- Headache
- Tiredness
- Discomfort when looking at bright lights.
The first sign of herpes zoster is usually localised pain without tenderness or any visible change to the skin.
After the onset of pain the rash may appear within 1-3 days. It starts as a crop of red papules. New lesions continue to erupt for several days within the distribution of the affected nerve, each blistering or becoming pustular then crusting over. It often makes a stripe or belt-like pattern on one side of the face or body.
The rash can last about 10 to 15 days.
Sometimes the rash can become infected.
Sometimes the pain is still there even after the rash goes away. If the pain lasts for more than three months, it is called post-herpetic neuralgia.
Treatment and Management
Being vaccinated is a safe and effective way to protect yourself against shingles.
Shingles is less contagious than chickenpox. The risk of spreading the disease is low if the rash is covered. When the rash has developed crusts, you are no longer infectious.
General Measures
- Rest and pain relief
- Protective ointment applied to the rash, such as petroleum jelly.
- Oral antibiotics for secondary infection
- Cover the rash (if possible)
- Avoid touching or scratching the rash
- Wash hands often to prevent the virus from spreading.
Avoid contact with these people until the rash has developed crusts:
- Pregnant women who have never had chickenpox or the chickenpox vaccine
- Premature or low birthweight babies
- Children who have not had chickenpox or the chickenpox vaccine
- People with weakened immune systems, such as people who:
- Have had chemotherapy
- Are taking other medicines that weaken their immune system
- Have had a transplant
- Are living with HIV.
As soon as you believe that someone may have shingles they must see their doctor immediately. Prompt anti viral treatment will ease the nerve damage and help to prevent the pain lasting for as long. Effective shingles treatments are available from your doctor and must be taken for the full course of treatment.
Your local pharmacist can support and advise to manage and minimise the effects of shingles, and will refer you to further help if products you have tried have not worked to ease your recovery from this painful and debilitating condition.